Which Type of Muscle Can Be Found Inside Organs
15.iii: Types of Muscle Tissue
- Folio ID
- 16811
Turn your eyes—a tiny movement, considering the clearly big and strong external eye muscles that control eyeball movements. These muscles have been called the strongest muscles in the human body relative to the work they practice. Nevertheless, the external eye muscles actually exercise a surprising amount of work. Eye movements occur virtually constantly during waking hours, specially when nosotros are scanning faces or reading. Center muscles are as well exercised nightly during the phase of sleep called rapid eye move sleep. External eye muscles can motion the eyes because they are fabricated mainly of musculus tissue.

What is Muscle Tissue?
Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that makes upward most of the tissues in the muscles of the human muscular organization. Other tissues in muscles are connective tissues, such as tendons that adhere skeletal muscles to bones and sheaths of connective tissues that comprehend or line musculus tissues. Only musculus tissue per se, still, has cells with the ability to contract.
There are three major types of muscle tissues in the human trunk: skeletal, shine, and cardiac musculus tissues. Effigy \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows how the 3 types of muscle tissues appear nether a microscope. When you read virtually each type beneath, yous volition acquire why the 3 types appear every bit they do.
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Skeletal musculus is muscle tissue attached to bones past tendons, which are bundles of collagen fibers. Whether you are moving your eyes or running a marathon, you are using skeletal muscles. Contractions of skeletal muscles are voluntary or under the witting command of the primal nervous organisation via the somatic nervous system. Skeletal muscle tissue is the almost common type of muscle tissue in the human body. By weight, an average adult male person is about 42 percent skeletal muscles, and the average adult female is nearly 36 percent skeletal muscles. Some of the major skeletal muscles in the human trunk are labeled in Figures \(\PageIndex{3}\) and Figure \(\PageIndex{four}\) and listed in Table \(\PageIndex{1}\).
| Muscles visible in Figure \(\PageIndex{iii}\) | Muscles visible in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) |
|---|---|
| rotator cuff (multiple muscles are office of this grouping) | levator scapulae |
| biceps brachii | rhomboids |
| brachialis | rotator cuff |
| pronator teres | triceps brachii |
| brachioradialis | gluteus maximus |
| adductor muscles | tibialis posterior |
| tibialis anterior | peroneus longus |
| deltoid | peroneus brevis |
| pectoralis major | trapezius |
| rectus abdominis | deltoid |
| abdominal external oblique | brachioradialis |
| iliopsoas | latissimus dorsi |
| quadriceps femoris | biceps femoris |
| peroneus longus | semitendinosus |
| peroneus bravis | semimembranousus |
| gastrocnemius | |
| soleus |
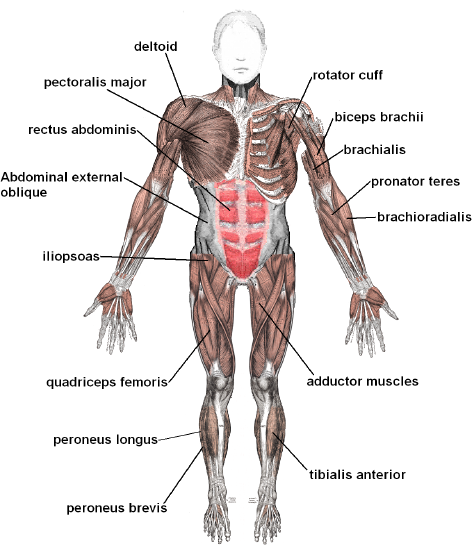
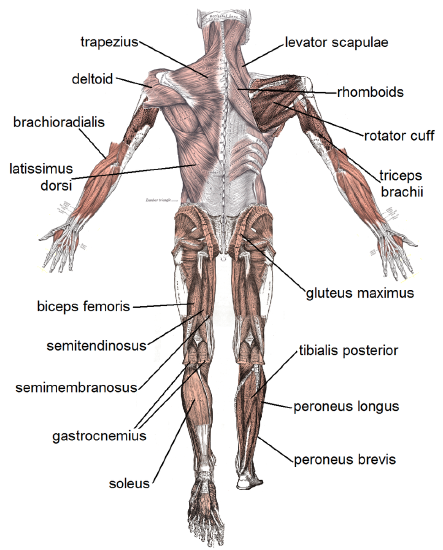
Skeletal Muscle Pairs
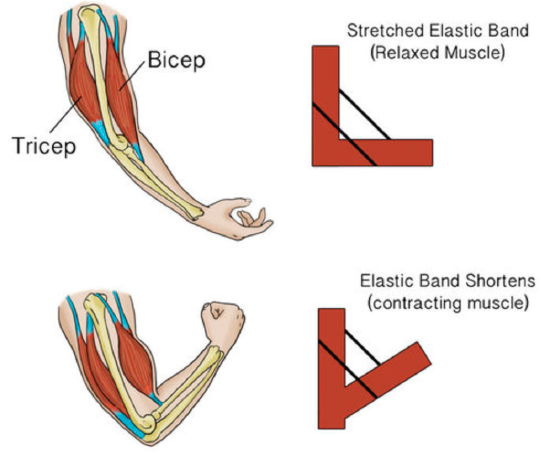
To move bones in contrary directions, skeletal muscles oft consist of muscle pairs that work in opposition to one another. For example, when the biceps muscle (on the front of the upper arm) contracts, it can cause the elbow joint to flex or bend the arm, as shown in Effigy \(\PageIndex{5}\). When the triceps muscle (on the back of the upper arm) contracts, information technology tin cause the elbow to extend or straighten the arm. The biceps and triceps muscles are examples of a musculus pair where the muscles work in opposition to each other.
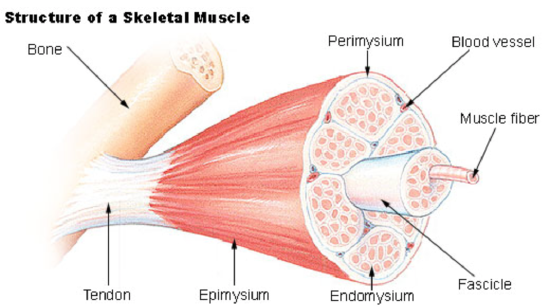
Skeletal Musculus Structure
Each skeletal musculus consists of hundreds — or even thousands — of skeletal musculus fibers, which are long, string-like cells. As shown in Effigy \(\PageIndex{6}\), skeletal muscle fibers are individually wrapped in connective tissue called endomysium. The skeletal muscle fibers are bundled together in units chosen muscle fascicles, surrounded by sheaths of connective tissue called perimysium. Each fascicle contains between ten and 100 (or even more!) skeletal muscle fibers. Fascicles, in turn, are bundled together to course private skeletal muscles, which are wrapped in connective tissue chosen epimysium. The connective tissues in skeletal muscles have a diversity of functions. They back up and protect musculus fibers, allowing them to withstand contraction forces by distributing the forces applied to the muscle. They also provide pathways for nerves and blood vessels to achieve the muscles. Also, the epimysium anchors the muscles to tendons.
The same bundles-within-bundles structure is replicated within each muscle cobweb. As shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\), a musculus fiber consists of a packet of myofibrils, which are themselves bundles of protein filaments. These protein filaments consist of thin filaments of the protein actin, anchored to structures called Z discs — and thick filaments of the protein myosin. The filaments are bundled together within a myofibril in repeating units called sarcomeres, which run from one Z disc to the next. The sarcomere is the basic functional unit of skeletal (and cardiac) muscles. It contracts as actin and myosin filaments slide over i another. Skeletal muscle tissue is said to be striated considering it appears striped. It has this advent because of the regular, alternate A (nighttime) and I (lite) bands of filaments arranged in sarcomeres inside the muscle fibers. Other components of a skeletal muscle cobweb include multiple nuclei and mitochondria.

Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Fibers
Skeletal muscle fibers tin can be divided into ii types, chosen slow-twitch (or blazon I) muscle fibers and fast-twitch (or type Two) muscle fibers.
- Deadening-twitch muscle fibers are dense with capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, a protein that stores oxygen until needed for musculus activeness. Relative to fast-twitch fibers, deadening-twitch fibers can carry more than oxygen and sustain aerobic (oxygen-using) activity. Slow-twitch fibers tin contract for long periods of time, but not with very much strength. They are relied upon primarily in endurance events, such equally distance running or cycling.
- Fast-twitch muscle fibers contain fewer capillaries and mitochondria and less myoglobin. This blazon of muscle fiber can contract rapidly and powerfully, simply it fatigues very speedily. Fast-twitch fibers can sustain but short, anaerobic (non-oxygen-using) bursts of activity. Relative to slow-twitch fibers, fast-twitch fibers contribute more than to muscle strength and have a greater potential for increasing mass. They are relied upon primarily in short, strenuous events, such as sprinting or weight lifting.
Proportions of fiber types vary considerably from muscle to muscle and from person to person. Individuals may be genetically predisposed to have a larger percentage of i blazon of muscle fiber than the other. Generally, an individual who has more slow-twitch fibers is better suited for activities requiring endurance. In contrast, an individual who has more fast-twitch fibers is better suited for activities requiring short bursts of power.
Shine Muscle
Smooth musculus is muscle tissue in the walls of internal organs and other internal structures such as claret vessels. When smooth muscles contract, they help the organs and vessels carry out their functions. When shine muscles in the stomach wall contract, they squeeze the nutrient inside the stomach, helping to mix and churn the food and break it into smaller pieces. This is an important part of digestion. Contractions of smooth muscles are involuntary, and so they are non under conscious control. Instead, they are controlled by the autonomic nervous organisation, hormones, neurotransmitters, and other physiological factors.
Structure of Smooth Muscle
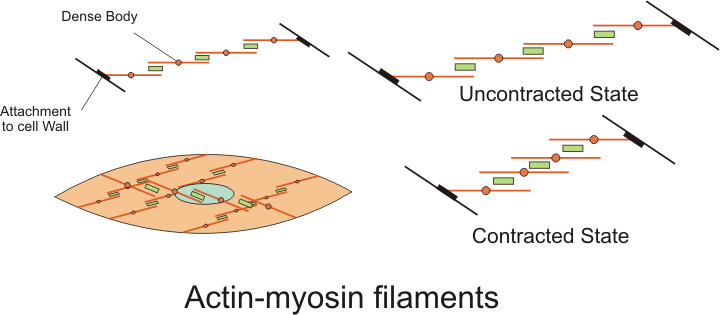
The cells that make up smooth musculus are generally called myocytes. Different the muscle fibers of striated muscle tissue, the myocytes of smoothen muscle tissue practise non have their filaments arranged in sarcomeres. Therefore, polish tissue is not striated. However, the myocytes of smooth musculus contain myofibrils, which contain bundles of myosin and actin filaments. The filaments cause contractions when they slide over each other, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\).
Functions of Smooth Muscle
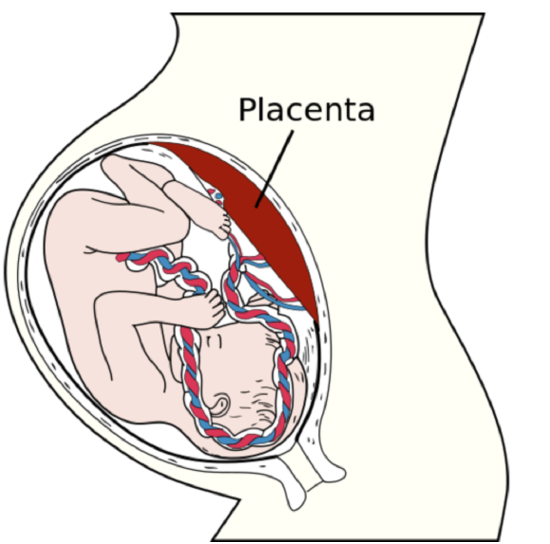
Unlike striated muscle, smooth muscle can sustain very long-term contractions. Smoothen muscle can likewise stretch and even so maintain its contractile office, which striated musculus cannot. An extracellular matrix secreted by myocytes enhances the elasticity of smooth muscle. The matrix consists of elastin, collagen, and other stretchy fibers. The ability to stretch and nonetheless contract is an important attribute of shine musculus in organs such as the stomach and uterus (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)), both of which must stretch considerably as they perform their normal functions.
The following list indicates where many polish muscles are plant, along with some of their specific functions.
- Walls of the gastrointestinal tract (such as the esophagus, stomach, and intestines), moving food through the tract by peristalsis.
- Walls of air passages of the respiratory tract (such as the bronchi), controlling the diameter of the passages and the volume of air that can pass through them
- Walls of organs of the male and female reproductive tracts; in the uterus, for example, pushing a baby out of the uterus and into the nativity canal
- Walls of the urinary organization structures, including the urinary float, allow the bladder to expand so it can hold more urine and then contract equally urine is released.
- Walls of blood vessels, controlling the bore of the vessels and thereby affecting blood flow and blood pressure
- Walls of lymphatic vessels, squeezing the fluid called lymph through the vessels.
- Iris of the eyes, controlling the size of the pupils and thereby the amount of lite entering the optics
- Arrector pili in the skin, raising hairs in pilus follicles in the dermis.
Cardiac Muscle
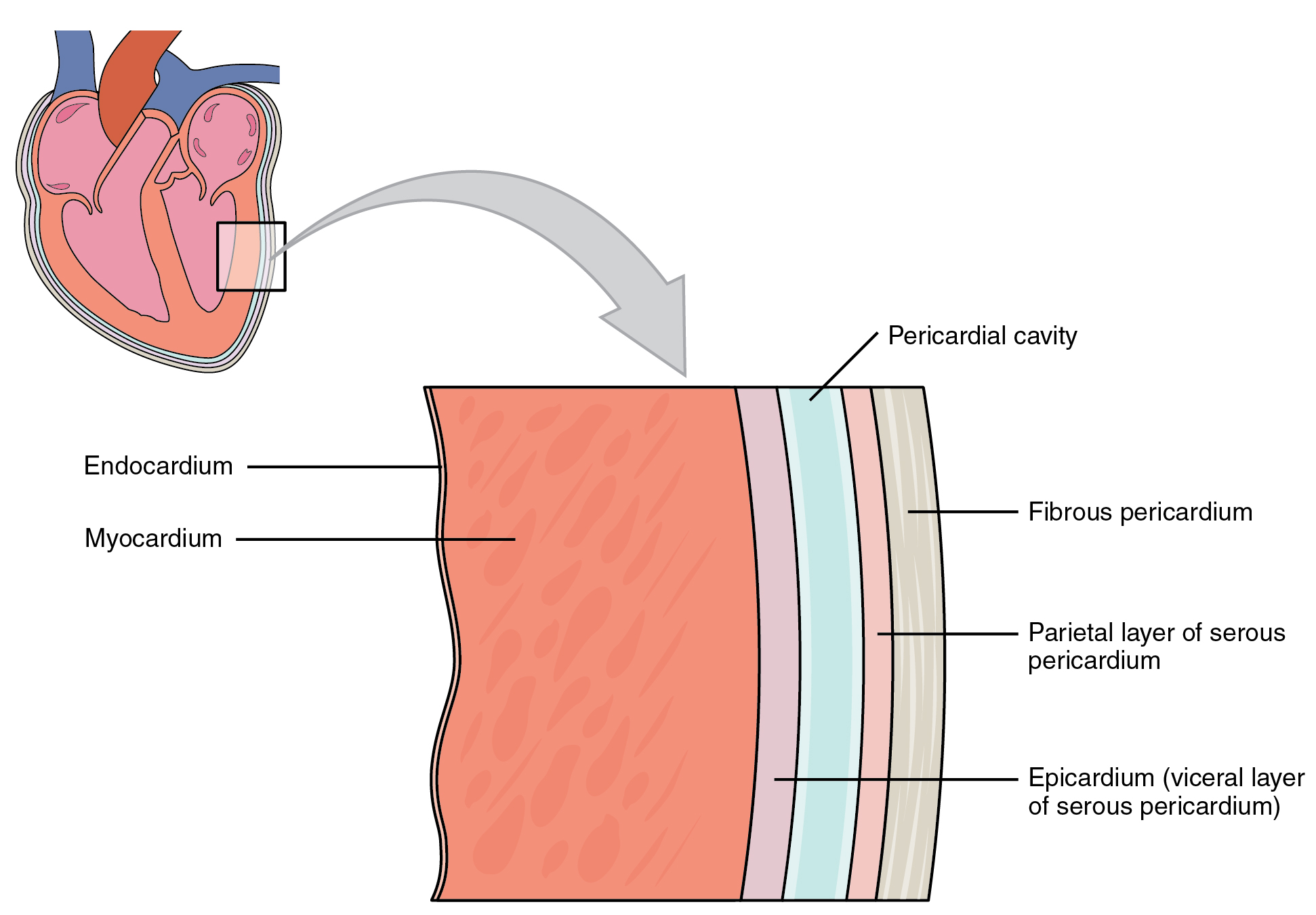
Cardiac muscle is found just in the wall of the center. It is also called myocardium. As shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\), the myocardium is enclosed within connective tissues, including the endocardium on the inside of the center and pericardium on the outside of the heart. When cardiac muscle contracts, the center beats and pumps blood. Contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscles. They are controlled by electric impulses from specialized cardiac muscle cells in the eye muscle expanse called the sinoatrial node.
Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated because its filaments are arranged in sarcomeres inside the musculus fibers. However, in cardiac muscle, the myofibrils are branched at irregular angles rather than arranged in parallel rows (as they are in skeletal musculus). This explains why cardiac and skeletal muscle tissues expect unlike from one another.
The cells of cardiac muscle tissue are arranged in interconnected networks. This organisation allows rapid transmission of electric impulses, which stimulate virtually simultaneous contractions of the cells. This enables the cells to coordinate contractions of the heart musculus.
The heart is the muscle that performs the greatest corporeality of physical work in a lifetime. Although the heart'southward ability output is much less than the maximum power output of some other muscles in the homo trunk, the heart does its piece of work continuously over an entire lifetime without rest. The cardiac musculus contains many mitochondria, which produce ATP for energy and aid the middle resist fatigue.
The human eye develops in a sequence of events that are controlled by communication amid different types of cells, including cells that volition become myocardium (the cardiac muscle that forms the wall of the eye) and cells that will become endocardium (the connective tissue that covers the inside surface of the myocardium). If communication among the cells is aberrant, it tin atomic number 82 to various heart defects, such as cardiac hypertrophy or abnormal enlargement of the center muscle. Cardiac hypertrophy causes the heart to thicken and weaken over time, and so information technology is less able to pump claret. Somewhen, heart failure may develop, causing fluid to build up in the lungs and extremities.
Abnormal prison cell communication is the machinery by which a mutation chosen PTPN11 leads to cardiac hypertrophy in disorder referred to as NSML (Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Lentigines). New inquiry past scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston has adamant which type of cell abnormalities occur that lead to NSML. In the research, the scientists engineered mouse models to express the PTPN11 mutation as they developed. The researchers manipulated the mouse models and so that the mutation was expressed only in cells that would develop into the myocardium in some of the mice. In contrast, in other mice, the mutation was expressed just in cells that would develop into endocardium. Unexpectedly, the heart's hypertrophy occurred only in the mice that expressed the mutation in endocardial cells, not in myocardial cells, which had long been assumed to exist the cells afflicted. The results of the enquiry propose potential targets for the handling of NSML. They may likewise assistance scientists understand the causes of other cardiac disorders that are much more than mutual than NSML.
Review
1. What is musculus tissue?
2. Where is the skeletal muscle found, and what is its general part?
3. Why practise many skeletal muscles piece of work in pairs?
iv. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle.
five. Relate muscle fiber structure to the functional units of muscles.
six. Why is skeletal musculus tissue striated?
7. Compare and contrast wearisome-twitch and fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibers.
8. Where is the smooth muscle institute? What controls the contraction of smooth muscle?
9. Compare and dissimilarity smooth muscle and striated muscle (such as skeletal musculus).
ten. Where is the cardiac musculus institute? What controls its contractions?
xi. Both cardiac and skeletal muscle tissues are striated, but they look different from i some other. Why?
12. The heart musculus is smaller and less powerful than another muscles in the body. Why is the eye the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in a lifetime? How does the heart resist fatigue?
13. Arrange the post-obit units within a skeletal musculus in order, from smallest to largest: fascicle; sarcomere; muscle fiber; myofibril
14. Give one example of connective tissue that is found in muscles. Depict one of its functions.
xv. True or False: skeletal muscle fibers are cells with multiple nuclei.
Explore More
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Book:_Human_Biology_%28Wakim_and_Grewal%29/15:_Muscular_System/15.3:_Types_of_Muscle_Tissue

0 Response to "Which Type of Muscle Can Be Found Inside Organs"
Post a Comment